Birth defects are serious problems that occur while a baby develops in utero (the womb). Around one in every 33 babies is born with a birth defect in the United States.
Birth defects can either affect the appearance of the child, the physiology of the organs, or the development of the child. Birth defects and other developmental disorders tend to occur in the first three months of pregnancy during the period when the organs are forming. Severe birth defects, causing 20 percent of infant deaths in the United States, are the leading cause of infant death. Some birth defects are harmless. Others require long-term medical treatment.
What are the causes of birth defects?
The following can result in birth defects:
- behaviors and lifestyle choices
- Exposure to drugs and chemicals
- Pregnancy infections
- genetics
- Combining these factors
Some birth defects are, however, difficult to determine what causes them.
Genetics
Genetic defects may occur at conception. These defects might happen at birth, or can also be passed on to the baby of a mother or father as a result of a mutation or change. A particular defect may be present in either parent’s family history.
Nongenetic causes
Despite the difficulty of precisely determining the causes of some birth defects, certain behaviors can increase the risk of birth defects. Examples of these behaviors include smoking, drinking alcohol while pregnant, and using illegal drugs. Other factors include contact with toxic chemicals and viruses.
Birth defects: What are the Risk Factors?

A woman who is pregnant has a slight chance of giving birth to a child with a birth defect. The risk increases in the following situations:
- families with a history of genetic disorders and birth defects
- During pregnancy, drug or alcohol use, smoking, or excessive drinking
- mothers aged 35 or older
- Pregnancy care is inadequate.
- Sexually transmitted infections including viral or bacterial infections resulting from untreated infections
- Use of isotretinoin and lithium, high-risk medications,
The risk of birth defects is also higher in women with pre-existing medical conditions, like diabetes.
Common birth defects in children
Most birth defects are broken down into structural or functional and developmental defects.
Structure-related defects are characterized by specific body parts that are missing or malformed. Common structural defects include:
- congenital heart defects
- When there is a visible opening or split in the lip or the roof of the mouth, this is called a cleft lip or palate.
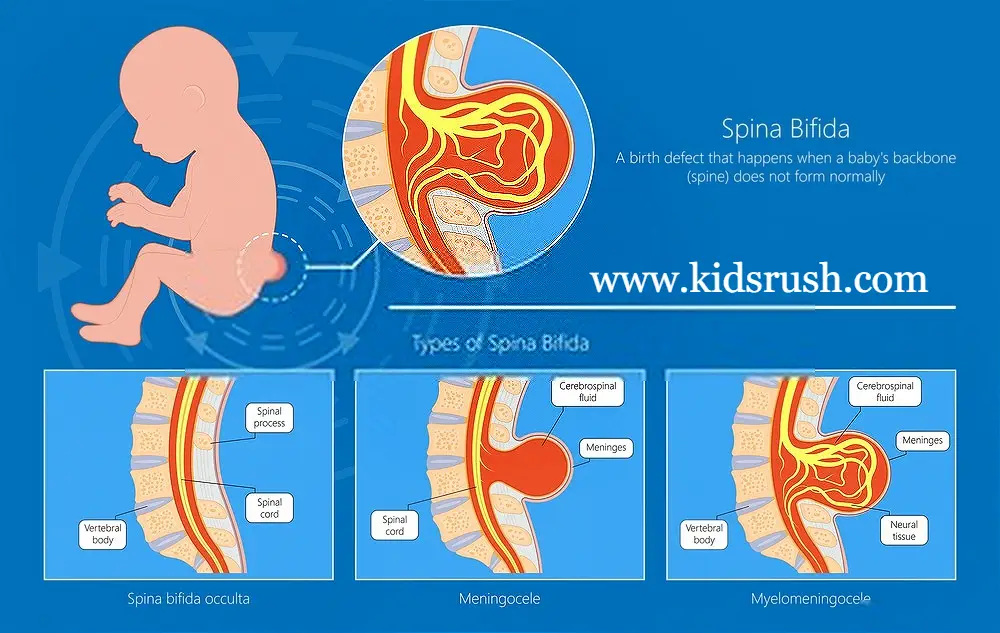
- A condition that occurs when the spinal cord fails to form properly is called spina bifida.
- An inwardly pointed foot is called clubfoot.
Functional birth defects can lead to sensory problems, nervous system problems, and metabolic anomalies. Metabolic defects affect the baby’s chemistry negatively. Some birth defects don’t become apparent until the child is two years old.
Birth defects that occur most commonly include:
- There is a delay in physical and mental development that is caused by Down syndrome.
- Sickle cell disease results in the red blood cells becoming misshapen
- A lung and digestive disease caused by cystic fibrosis
- Defects aren’t always visible until months or even years after the child is born, but some birth defects can lead to severe physical problems and psychological problems if left untreated.
Birth defects: Diagnosis

There are over one hundred birth defects that can be detected with prenatal ultrasounds. Additional tests, such as blood tests and amniocentesis, may be available for women who have more than high-risk pregnancies due to family history or advanced maternal age.
The preexisting mother may have an infection or another condition that promotes birth defects. A physical examination and hearing tests may detect birth defects after the baby is born. A newborn blood test can identify birth defects ahead of symptoms.
Birth defects can be detected with certainty only after birth. However, prenatal screening may identify defects even when none are present. A screening test can also identify defects in a false positive fashion.
What is the treatment for birth defects?
There are different treatment options for different conditions, as severe birth defects may need to be treated immediately after birth. Mild birth defects, however, do not usually affect someone’s overall quality of life. Birth defects can cause long-term disabilities or even death, such as cerebral palsy or spina bifida. Discuss with your doctor your child’s concerns with a doctor.
Medications: Sometimes, medication has prescribed to the mother to help cure an abnormality before birth to treat some birth defects. Medications may also be used to lower the risk of complications for certain defects.
Surgeries: A surgeon can fix a birth defect or relieve a problematic condition. Some people born with physical birth defects, such as a cleft lip, undergo cosmetic (non-medical) surgery. Many babies with a heart abnormality will also need surgery.
Home care: New parents should follow particular instructions regarding feeding, bathing, and monitoring for newborns with birth defects. [1]
What can be done to prevent birth defects?
Even though some birth defects cannot be prevented, there are various steps that women can take to lower their chances of having an affected baby. During pregnancy, women undergo folic acid supplementation so that defects of the spine and the brain can be prevented. Prenatal vitamins are also advised.
While pregnant women should avoid tobacco, alcohol, drugs, and tobacco, some medications can cause serious birth defects in unborn children. If you are taking any medications, especially over-the-counter or supplements, share this information with your doctor.
Some vaccines can prevent birth defects, so you should seek the advice of your doctor when pregnant. There is a theoretical risk of harm to a developing fetus with some live-virus vaccines, so you don’t want to receive these when you are pregnant.
Diabetes patients should take special care to manage their health, especially women who are overweight and who need to maintain a healthy weight during pregnancy.
Regular prenatal plans are essential. If you are experiencing an especially high-risk pregnancy, your doctor may run a prenatal scan to detect defects earlier or treat them after birth.
Medical genetic counseling
A genetic counselor can assist couples faced with family histories or factors connected to birth defects. They can also advise couples concerned about the prospects of having children or expecting children. Genetic counselors evaluate family history and medical records to determine the likelihood that your child will be born with defects.
